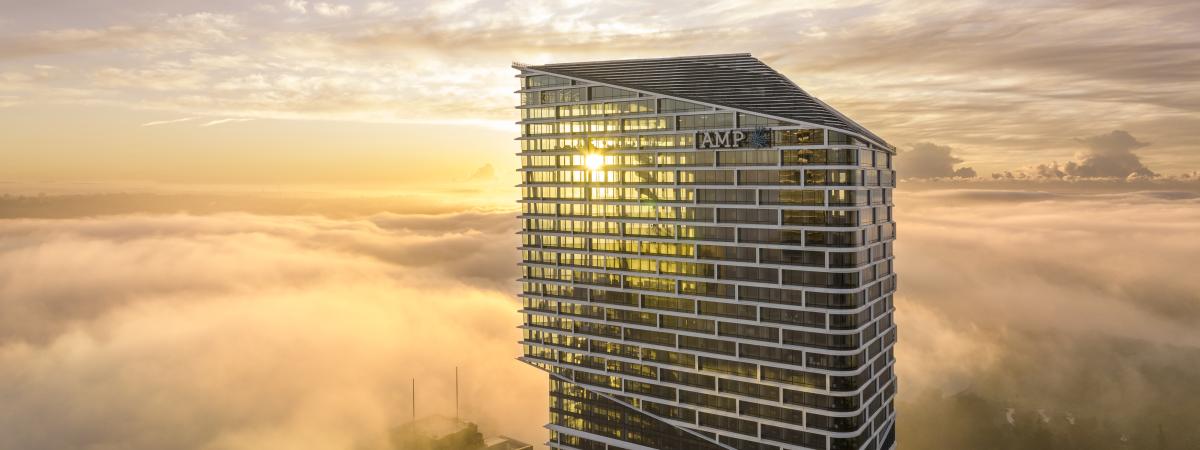
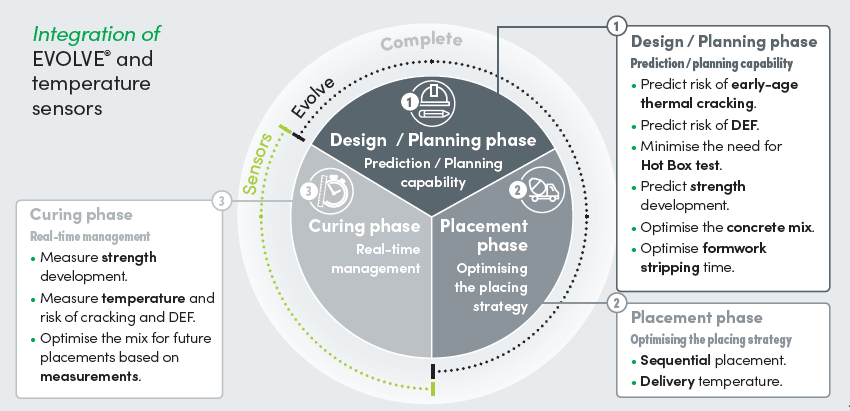
EVOLVE™ thermal modelling provides valuable insights into how temperature rise within a concrete element and how concrete mixes can be modified or preventive measures applied to manage the risk of early-age thermal cracking.
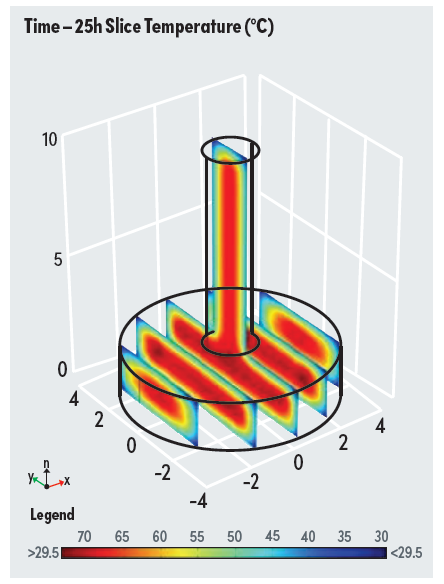
EVOLVE™ is a 3D simulation finite element model designed to predict temperature development and differences, to facilitate a better understanding of the risk of thermal cracking of concrete.
Enhanced by extensive experimental testing of in-house materials conducted by Boral in collaboration with the University of NSW, EVOLVE™ offers greater accuracy compared to models developed using international materials.
This innovative tool enhances the durability and performance of concrete structures, making it a valuable asset for construction projects.
Technical Background
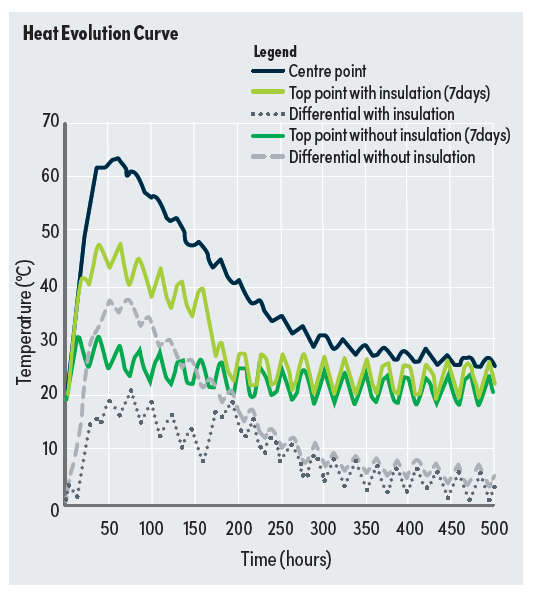
Temperature rises can create a range of issues for concrete. For example, there may be concerns with temperature rise in large concrete elements during cement hydration. It may be necessary to limit the peak temperature to prevent Delayed Ettringite Formation (DEF) from forming in the future, potentially leading to concrete expansion and cracking. Another issue may be the temperature differential between the hot interior and cold exterior of concrete, which can cause tensile stresses on the exterior. If these stresses exceed the tensile strength of the concrete, cracking can occur.
These issues can result in significant problems, including early‑age cracking and the production of expansive products that can lead to cracking after a few years. Rectifying such problems can be costly, requiring extensive rework.
These issues can result in significant problems, requiring extensive rework to rectify. Addressing these issues during the design stage is essential, and Boral's proprietary EVOLVE™ thermal modelling solution is designed to deliver this capability.
Customer insights
A look at our clients’ perspectives
EVOLVE™ has been utilised in over 100 projects nationally, including One Circular Quay and Atlassian Central, receiving excellent customer feedback.
By testing on local materials, EVOLVE™ provides greater certainty in predicting thermal behaviour in higher-risk structures. This results in reduced placing and curing costs through minimising thermal controls required by consultants, such as chilled water and ice.
Analysing cost impacts
The benefits of using EVOLVE™ can lead to significant time and cost savings on construction projects. By addressing heat-related issues through changes in mix designs, such as the addition of supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), additional testing, special construction methods, and increased batching costs, EVOLVE™ helps mitigate the risk of early-age thermal cracking.
The cost associated with resolving heating issues can be substantial, but EVOLVE™ provides a proactive solution that enhances the durability and performance of concrete structures, ultimately reducing long-term maintenance and repair costs.

In the Media
Engineers Australia published an article featuring Dr Ali Nezhad, Head of Sustainability and Innovation at Boral, discussing the importance of minimising cracking to maximise long-term performance. Dr Nezhad shared the rationale for EVOLVE™, a modelling tool developed by Boral to predict the temperature differential of concrete more effectively. Watch the video interview for more insights.




